Magnetic components are passive elements that rely on an internal magnetic field to alter electrical current. They play a critical role in many electronic devices, equipment, and systems. Some of the industries that often make use of them include: Appliances: Magnetic components play critical roles in both common household and advanced industrial appliances (ranging from…
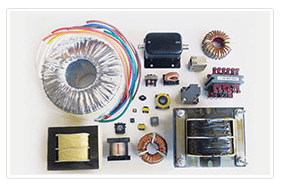
Manufacturing & Magnetics – An Important Industry Outlook
With 2017 officially closed, now is the time to look towards industry predictions in the new year. Industry Outlook Predictions Projections for 2018 show positive outlooks for three of the main industries MPS serves. The renewable energy sector, both globally and within the U.S., will always be at the forefront of debate and conversation. Renewables (in…
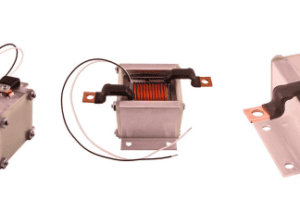
How to Tell if Your High Current Inductor is Really High Current
You’ve selected an inductor, but how can you tell if a high current inductor truly is high current? It’s crucial to confirm that the inductor you’re using matches the specifications you need and that they are capable of performing accurately. Certain manufacturers use data sheets to mention the saturation current on the inductor “can be…
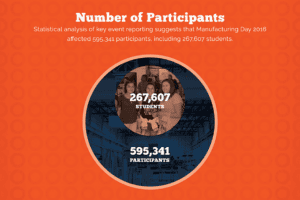
Help the Manufacturing Industry Celebrate National Manufacturing Day!
As the first Friday in October, National Manufacturing Day 2017 will happen on October 6th. As a prominent electronics component manufacturer, MPS Industries is happy to spread the word about NMD. This year the event promises to be a day full of education and encouragement for all attendees. What MFG DAY Means for the Industry…
The Automotive Recovery, Powered by MPS
Recent news and trends all point to a giant recovery for the American auto industry. Most major automakers saw moderate to large sales increases in 2012; one market research firm, Polk, now expects new car sales to increase by 6.6% in 2013, thanks to a recovering economy and growth in the pickup truck and midsize…
Electronics and the eCommerce Revolution
With Black Friday and Cyber Monday in the rear-view mirror, the holiday shopping season has hit full stride. As expected, these two highly anticipated shopping days did not disappoint in 2012; in fact, Cyber Monday was most likely the busiest eCommerce day in history up 30% from last year. In addition, both days proved that…
